Foreword
Why are phages making a comeback?
Bacteriophage, we all know that it is a bacteria as the host of the virus, widespread in nature. We can apply it to clinical treatment by using some of its characteristics: the characteristics of fighting against bacteria are strong specificity, it does not destroy the normal flora and does not infect eukaryotic cells; the speed of infection and lysis of bacteria is fast, at the same time has the ability of self-proliferation. The return of bacteriophages to the fight against bacteria after more than 100 years can be attributed to the prevalence of superbugs in our environment. We carry out phage clinical trials to study the phage-related mechanism of action, and hope that it will become a new means of antibacterial therapy. On the road to antimicrobial therapy, phages do not follow the traditional path of antibiotics. The antibiotic has the broad-spectrum, the selectivity are many, the compatibility is strong and so on the characteristic, certainly these are speaking to the general bacteria. With decades of research and production history, we have a clear understanding of the research background and mechanism of antibiotics, and the clinical application is also handy. However, the long-term abuse of antibiotics has led to the development of drug resistance in many aspects, such as the production of β-lactam enzymes, inactivation of enzymes, biofilm formation, bacterial wall thickening, etc. , blockage of the drug into the channel and through the cell membrane efflux pump will be drug efflux and so on. Once a bacterium has these functions, it may become a“Superbug”. Phages are the natural killers of these target bacteria. They can degrade biofilms, facilitate bacterial expulsion and tissue repair; their self-proliferative characteristics do not require long-term administration; therefore, phage therapy has obvious advantages.
Characteristics of superbugs in genitourinary tract infections
There are several clinical urinary tract infection of urinary tract infections (Uti) : 1) Upper Uti, lower UTI, and total UTI according to the site of infection; 2) simple UTI and complex UTI according to the presence or absence of a specific cause. The main causes of complex urinary tract infection are urinary obstruction, urinary system malformation or dysfunction, long-term indwelling urinary catheter and device operation, tumor, chemotherapy and radiotherapy history, etc. . 3) according to the correlation classification of secondary infection: A, after treatment, the symptoms disappeared and the urine bacteria were negative, and the symptoms reappeared within 6 weeks. B, the number of urinary bacteria ≥10 ^ 5 CFU/ml, and the same strain as the last time (the same strain and the same serotype, or the same drug sensitivity spectrum) belong to recurrent infections. Urogenital superbacterial infections are related to complex causes. Such infections have many causes, such as complex pathogens, most of them are whole urinary tract infections, deep infection sites, difficult to clear, recurrent attacks, long course of disease, and basically low immunity of patients, so clinical treatment is difficult.
2. Bacteriophage therapy for urogenital infections
At present, the bacteriophage therapy of urogenital tract infection adopts the way of local medication, treatment was achieved by 3 routes of administration (Fig. 1) : 1) transurethral instillation of the bladder for bladder and prostate infections; 2) transurethral-pelvic retrograde instillation for total urinary tract infections; and 3) percutaneous nephrostomy instillation for total urinary tract infections. These in clinical application has been formed more mature operating standards.
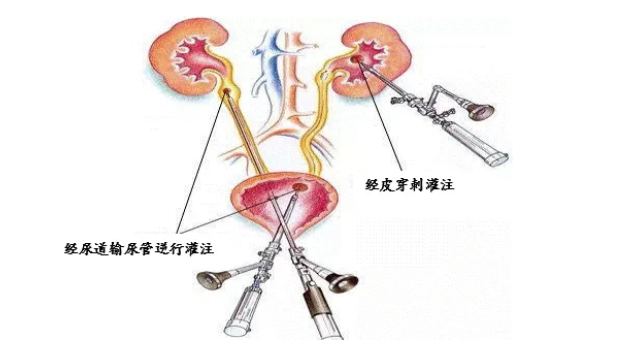
Fig. 1 mode of administration of urogenital phage therapy
3. Key points in clinical treatment of bacteriophages
3.1 pinpointing“Superbugs”
In clinical practice, it is necessary to take multiple urine samples to determine whether the acquired bacteria are randomly infected or colonized by the patient; analyze whether there are multiple infections; the urinary system is divided into the left and right kidneys and the bladder, urethra, different parts may have different bacterial infections, multiple sampling, you can get different parts of the infection bacteria, so as to configure a strong adaptability of phage. In the process of bacterial culture, multiple isolation and selection of a number of monoclonal, but also better with the capture of the target bacteria.Our requirements are: accurate, comprehensive. For patients with severe mental symptoms or depression, the treatment process is prone to doctor-patient conflict, how to better deal with such patients? Our approach is that no matter how severe the clinical complaints of patients are,If no pathogenic bacteria can be cultured, we do not accept clinical enrollment; if pathogenic bacteria can be cultured and a lytic phage is screened, we accept enrollment. Through our treatment, the removal of pathogenic bacteria, the treatment of patients with mental illness is beneficial.
3.2 Screening for lytic phages, the reservoir phages of our phage library, has been whole genome sequencing to exclude resistant and deleterious genes. The principle of phage screening: under various conditions and conditions, through the bactericidal curve of phage, select strains with excellent lysis effect and not easy to tolerate, and take into account the morphology of phage to determine its stability, to obtain a cocktail of preferred phages.
3.3 Another important part of phage therapy is how to deliver the phage to the infected site of the patient to achieve full coverage of the infected site. The endoscopic technique of urology plays a very important role: it has the advantage of being minimally invasive, visual, and able to observe what is going on in the urogenital tract of the patient for precise catheterization and drug administration (Fig. 2) . We also combined the endoscopic surgical treatment to relieve the infectious etiology of the patient, and observed the changes of the urogenital epithelial tissue of the patient before and after treatment by laparoscopy to evaluate the curative effect.
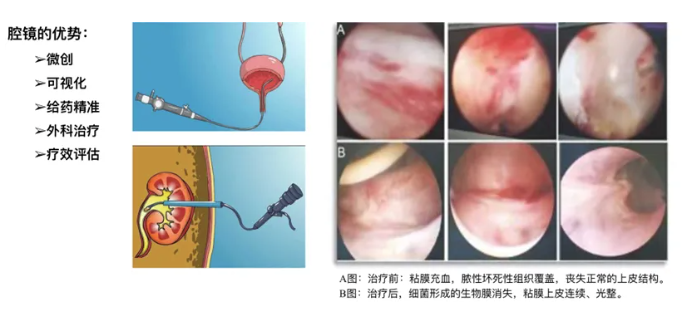
Fig. 2 application of endoscopy in phage therapy
In 2021, we admitted a patient with a long history of diabetes who was bedridden due to a patellar fracture. Since May, 2021, the patient has experienced recurrent fever, frequent urination, painful urination, dysuria, urinary retention, and residual urine of more than 200 ml. Urine bacterial culture: multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection, and antibacterial treatment in an outside hospital for more than two months, the body temperature does not drop, requests the bacteriophage treatment to transfer to our hospital. On admission, a CT scan of the urinary tract revealed a large cast stone in the right kidney, and we analyzed this patient for urinary tract infection complications, percutaneous nephrolithotomy is the first choice in urology for the treatment of multiple kidney stones and cast stones, but it is contraindicated if the patient is in a period of severe infection, we developed a treatment protocol: phage + surgical treatment; after two rounds of phage treatment, the patient’s body temperature was controlled, and the amount of urine bacteria was significantly reduced. We performed percutaneous nephrolithotomy with the support of negative pressure suction equipment, before and after the treatment of imaging examination, renal calculi were more thoroughly cleared. After more than a year of follow-up, the patient’s body temperature remained normal, urinary system symptoms improved significantly, the amount of bacteria in urine decreased significantly, and there was no need to take antibiotic maintenance therapy. Therefore, we believe that phage therapy is clearly beneficial for such patients.
4. End points of phage therapy
Two end points were set in our clinical trial: 1) the primary end point: complete clearance of the target organism. That is, both consecutive secondary bacterial cultures were negative after phage therapy; 2) secondary end points: significant improvement in clinical symptoms; I. Discharge/transfer from ICU for improvement; II. Improvement of urinary system symptoms such as: Return of body temperature to normal, return of urine to normal, marked improvement of urinary pain and low back pain (upper urinary tract infection) ;. Laparoscopy and imaging examination showed significant improvement of the lesions
Conclusion
Bacteriophage antibacterial therapy still has many problems waiting for us to study, we hope that it can enter the clinical treatment as soon as possible, so that the majority of infected patients benefit.
That’s all for today. If you find this article useful, feel free to follow it, like it, watch it, share it with friends, or find out more about kidney transplantation. See you next time.
Bacteriophage antibacterial therapy still has many problems waiting for us to study, we hope that it can enter the clinical treatment as soon as possible, so that the majority of infected patients benefit.
That’s all for today. If you find this article useful, feel free to follow it, like it, watch it, share it with friends, or find out more about kidney transplantation. See you next time.